BASIC EXCEL SKILLS
Now days, any job requires basic Excel skills. These basic Excel skills are – familiarity with Excel ribbons, ability to enter and format data, calculate totals summaries thru formulas and functions, highlight data that meets certain conditions, creating simple reports, charts, understanding the importance of keyboard shortcuts, productivity tricks etc.
Three most important components of Excel which you need to understand first:
1. Workbook
A workbook is another word for your Excel file. A workbook is a separate file just like every other application has. Each workbook contains one or more worksheets. You can also say that a workbook is a collection of multiple worksheets or can be a single worksheet.
You can add or delete worksheets, hide them within the workbook without deleting them, and change the order of your worksheets within the workbook.
2. Worksheet
A worksheet is made up of individual cells which can contain a value, a formula, or text. Each Excel workbook can contain multiple worksheets.
It also has an invisible draw layer, which holds charts, images, and diagrams. Each worksheet in a workbook is accessible by clicking the tab at the bottom of the workbook window.
In addition, a workbook can store chart sheets; a chart sheet displays a single chart and is accessible by clicking a tab.
3. Cell
A cell is a smallest but most powerful part of a spreadsheet. You can enter your data into a cell either by typing or by copy-paste.
Data can be a text, a number, Special character or a date. You can also customize it by changing its size, font color, background color, borders, etc.
Every cell is identified by its cell address, cell address contains its column number and row number (If a cell is on 1st row and on column A, then its address will be A1).
Window Components
Before you start using it, it’s really important to understand that what’s where in its window.
So ahead, we have the all major component which you need to know before entering the world of Microsoft Excel.
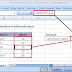
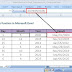
1. Active Cell
A cell is which currently selected. It will be highlighted by a rectangular box and its address will be shown in the address bar.
You can activate a cell by clicking on it or by using your arrow buttons. To edit a cell, you double-click on it or use F2 to as well.
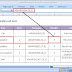
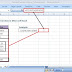
2. Column
A column is a vertical set of cells. A single worksheet contains 16,384 total columns.
Every column has its own alphabet for identity, columns are numbered from A on-wards and keeps on increasing as you keep entering data. After Z, it will start the series of AA, AB and so on. Maximum limit is 16,384 columns. You can select a column clicking on its header.
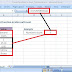
3. Row
A row is a horizontal set of cells. A single worksheet contains 10,48,576 total rows. Every row has its own number for identity, rows are numbered from 1 on-words and keeps on increasing as you keep entering data. Maximum limit is 10,48,576 rows.
You can select a row clicking on the row number marked on the left side of the window.
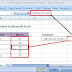
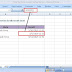
4. Fill Handle
It’s a small dot present on the lower right corner of the active cell. It helps you to fill numeric values, text series, insert ranges, insert serial numbers, etc.
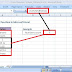
5. Address Bar
The address bar is the small input bar at the left side of the window.
It shows the address of the active cell. If you have selected more than one cell, then it will show the address of the first cell in the range.
6. Formula Bar
Formula bar is an input bar, below the ribbon. It shows the content of the active cell and you can also use it enter a formula in a cell.
7. Title Bar
This lies in the middle and at the top of the window. The title bar will show the name of your workbook, followed by the application name (“Microsoft Excel”).
8. File Menu
The file menu is a simple menu as like all other applications. It contains options like (Save, Save As, Open, New, Print, Excel Options, Share, etc).
9. Quick Access Toolbar
A toolbar to quickly access the options is which you frequently use. You can add your favorite options by adding new options to quick access toolbar.
10. Ribbon Tab
Starting from the Microsoft Excel 2007, all the options menus are replaced with the ribbons. Ribbon contains commands organized in three components - Tabs, Groups and commands. Ribbon tabs are the bunch of specific option group which further contains option. The tabs on the ribbon are: File, Home, Insert, Page layout, Formulas, Data, Review and View.
11. Worksheet Tab
This tab shows the all the worksheets which are present in the workbook. By default you will see, three worksheets in your new workbook with a name of Sheet1, Sheet2, Sheet3 respectively.
12. Status Bar
It is a thin bar at the bottom of the Excel window. It will give you an instant help once you start your working in Excel. This displays the sheet information as well as the insertion point location. From left to right, this bar can contain the total number of pages and words in the document, language etc.
Now days, any job requires basic Excel skills. These basic Excel skills are – familiarity with Excel ribbons, ability to enter and format data, calculate totals summaries thru formulas and functions, highlight data that meets certain conditions, creating simple reports, charts, understanding the importance of keyboard shortcuts, productivity tricks etc.
Three most important components of Excel which you need to understand first:
1. Workbook
A workbook is another word for your Excel file. A workbook is a separate file just like every other application has. Each workbook contains one or more worksheets. You can also say that a workbook is a collection of multiple worksheets or can be a single worksheet.
You can add or delete worksheets, hide them within the workbook without deleting them, and change the order of your worksheets within the workbook.
2. Worksheet
A worksheet is made up of individual cells which can contain a value, a formula, or text. Each Excel workbook can contain multiple worksheets.
It also has an invisible draw layer, which holds charts, images, and diagrams. Each worksheet in a workbook is accessible by clicking the tab at the bottom of the workbook window.
In addition, a workbook can store chart sheets; a chart sheet displays a single chart and is accessible by clicking a tab.
3. Cell
A cell is a smallest but most powerful part of a spreadsheet. You can enter your data into a cell either by typing or by copy-paste.
Data can be a text, a number, Special character or a date. You can also customize it by changing its size, font color, background color, borders, etc.
Every cell is identified by its cell address, cell address contains its column number and row number (If a cell is on 1st row and on column A, then its address will be A1).
Window Components
Before you start using it, it’s really important to understand that what’s where in its window.
So ahead, we have the all major component which you need to know before entering the world of Microsoft Excel.
1. Active Cell
A cell is which currently selected. It will be highlighted by a rectangular box and its address will be shown in the address bar.
You can activate a cell by clicking on it or by using your arrow buttons. To edit a cell, you double-click on it or use F2 to as well.
2. Column
A column is a vertical set of cells. A single worksheet contains 16,384 total columns.
Every column has its own alphabet for identity, columns are numbered from A on-wards and keeps on increasing as you keep entering data. After Z, it will start the series of AA, AB and so on. Maximum limit is 16,384 columns. You can select a column clicking on its header.
3. Row
A row is a horizontal set of cells. A single worksheet contains 10,48,576 total rows. Every row has its own number for identity, rows are numbered from 1 on-words and keeps on increasing as you keep entering data. Maximum limit is 10,48,576 rows.
You can select a row clicking on the row number marked on the left side of the window.
4. Fill Handle
It’s a small dot present on the lower right corner of the active cell. It helps you to fill numeric values, text series, insert ranges, insert serial numbers, etc.
5. Address Bar
The address bar is the small input bar at the left side of the window.
It shows the address of the active cell. If you have selected more than one cell, then it will show the address of the first cell in the range.
6. Formula Bar
Formula bar is an input bar, below the ribbon. It shows the content of the active cell and you can also use it enter a formula in a cell.
7. Title Bar
This lies in the middle and at the top of the window. The title bar will show the name of your workbook, followed by the application name (“Microsoft Excel”).
8. File Menu
The file menu is a simple menu as like all other applications. It contains options like (Save, Save As, Open, New, Print, Excel Options, Share, etc).
9. Quick Access Toolbar
A toolbar to quickly access the options is which you frequently use. You can add your favorite options by adding new options to quick access toolbar.
10. Ribbon Tab
Starting from the Microsoft Excel 2007, all the options menus are replaced with the ribbons. Ribbon contains commands organized in three components - Tabs, Groups and commands. Ribbon tabs are the bunch of specific option group which further contains option. The tabs on the ribbon are: File, Home, Insert, Page layout, Formulas, Data, Review and View.
11. Worksheet Tab
This tab shows the all the worksheets which are present in the workbook. By default you will see, three worksheets in your new workbook with a name of Sheet1, Sheet2, Sheet3 respectively.
12. Status Bar
It is a thin bar at the bottom of the Excel window. It will give you an instant help once you start your working in Excel. This displays the sheet information as well as the insertion point location. From left to right, this bar can contain the total number of pages and words in the document, language etc.

.png)




No comments:
Post a Comment